Blockchain
Experts Warn of Vulnerabilities about Ethereum Blockchain Security

Experts warn of vulnerabilities about Ethereum blockchain security, raising concerns about the safety of billions of dollars in cryptocurrency and the integrity of decentralized applications built on the platform.
A recent poll by Galaxy Digital researcher Christine Kim, on the social network “X” – former Twitter, reveals significant misconceptions within the Ethereum community about how much staked Ethereum (ETH) is necessary to secure the network.
Vulnerabilities of Ethereum: Less Staked ETH Needed for Attack Than Many Believe
Respondents displayed the following beliefs about Ethereum’s security:
- 44.9% believed that securing Ethereum requires 100% of all ETH staked, amounting to $110 billion, 31.4 million ETH.
- 20.4% thought 66.6% of staked ETH was sufficient, equivalent to $73.4 billion, 20.9 million ETH.
- 34.7% felt that only 33.3% of staked ETH, or $36.7 billion, 10.4 million ETH, was required for security.
Addressing these misconceptions, Christine Kim emphasized the actual vulnerabilities of Ethereum’s Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism in a detailed follow-up. She highlighted that an attacker can disrupt finality with 33% of the total stake, prolong a chain split with 50%, and double spend with 66% of the total stake.
Kim added that security primarily depends on the network’s ability to penalize stakers by burning large amounts of the locked value. The worse the attack, the more value stakers stand to lose.
It is crucial to comprehend the true significance of the situation, with a pun intended. Further elaboration from the Ethereum Foundation explains the technical underpinnings of these vulnerabilities.
An article by the foundation states that attackers using >= 33% of the total stake make all attacks mentioned more likely to succeed.
If the amount exceeds this limit, it would be a more precise and concise way of getting the same meaning so they can prevent the chain from finalizing without having to control the actions of the other validators.
For attacks involving 34% of the total stake, the article detailed a possible scenario of “double finality” where an attacker can manipulate the validation of two conflicting blockchain forks at the same time. This kind of attack is characterized by significant coordination and control over the timing of messages within the network, posing a high risk due to the potential slashing of the attacker’s entire staked amount.
Higher levels of controlled staking, such as 50% and 66%, increase the potential for more severe disruptions, including sustained chain splits and transaction censorship or reversal.
The foundation’s article elaborates that at >50% of the total stake, the attacker could dominate the fork choice algorithm, enabling them to censor certain transactions, do short-range reorgs, and extract maximum MEV by reordering blocks in their favor.
Ethereum Blockchain Security: The Power of Community Consensus
To protect the Ethereum network from security risks, it has an “inactivity leak” mechanism that gradually reduces the stake of inactive or malicious validators. Additionally, if the chain splits, the Ethereum community uses social consensus to decide which chain to follow.
These revelations underscore the importance of community awareness and technical safeguards in maintaining the security and integrity of the Ethereum network. While Ethereum’s PoS system offers several security advantages, it also requires vigilant monitoring and readiness to act against potential attacks.
As the Ethereum staking landscape evolves, several key trends have emerged, reshaping how stakeholders interact and benefit from the staking process.
The Rise of Re-staking and the Challengers to Lido’s Dominance
Tom Wan, researcher at 21.co, highlighted these trends in a recent post:
- Increase in Re-staking Popularity: Since 2024, there has been a significant shift towards re-staking in the Ethereum ecosystem.
- Re-staking contributions have grown from 10% to 60% of the total staked ETH. Eigenlayer, in particular, has risen to prominence as the second-largest DeFi protocol on Ethereum, holding a $15 billion Total Value Locked (TVL), which represents 13% of all staked ETH.
- The decline in Lido’s Market Share: The rise of liquid restaking protocols has noticeably impacted Lido’s dominance in the Ethereum staking market. Lido’s share has fallen below 30%, influenced by the growth of new platforms like Etherfi, which has become the second-largest withdrawer of stETH since 2024, totaling withdrawals of 108k stETH.
- Centralized Exchange (CEX) Staking Decline: The prevalence of centralized exchanges in ETH staking has decreased from 29.7% to 25.8% since 2024. Kiln Finance recently surpassed Binance to become the third-largest ETH staking entity. Ether.fi is gaining market share and is positioned to challenge Binance’s former dominance shortly.
In conclusion, the Ethereum community must be aware of the actual vulnerabilities of the blockchain’s security and take necessary measures to protect the network.
The trend towards re-staking, decline in Lido’s market share, and centralized exchange staking decline are significant developments that will shape the future of Ethereum’s staking landscape.
Blockchain
5 Reasons Why Delta Exchange is the Easiest Platform for Crypto Trading Strategies in the Indian Market
Crypto trading in India has grown exponentially in the last few years. In 2025, the market pulled in $258 million in revenue and is on track to hit nearly $732 million by 2033, growing at a 14.3% CAGR from 2026 onwards. That kind of money doesn’t come from people buying Bitcoin on a whim and hoping for a lucky spike. It comes from traders who plan entries, manage exits, build hedges, and run full-blown crypto trading setups.
This shift has created a new problem. Most Indian crypto exchange apps still feel built for basic spot buying without any advanced features to try. You open five tabs, check prices on one app, place orders on another, track risk on a third, and hope nothing slips through.
Delta Exchange transforms the story here. Instead of spots, Delta offers a safe trading platform to explore crypto derivatives (futures and options) across major currencies.
Let’s understand more about Delta Exchange and why so many Indian traders end up sticking with it once they try it.
Why Try Crypto Trading Strategies on Delta Exchange
Ranked among the top Indian crypto exchanges, Delta Exchange offers a range of features and analytics tools to simplify your crypto trading experience.
Here’s why many traders trust Delta Exchange:
- INR trading keeps things simple
If you’ve ever had to convert INR to USDT or USD just to trade Bitcoin, you know the hassle. Delta Exchange lets you deposit and withdraw in INR directly via UPI, IMPS, NEFT, and bank transfer, with your margin and profits shown in INR.
That means no awkward crypto conversions or extra wallets – you fund your account straight from your bank and start crypto trading like it’s normal money.
- Algo trading bots that actually work
Automation can save hours and reduce emotional stress and decisions, especially with fast moves in crypto F&O. Delta Exchange supports algo trading through APIs and bot integrations from platforms like TradingView and Tradetron.
You can link your trading strategy to webhooks or APIs and let bots place trades for Bitcoin futures or other crypto options even when you’re away. If you want systematic, repeatable strategies with fewer missed opportunities, this setup feels practical and real.
And the best part? You don’t need to have any coding knowledge or degree – API Copilot does it all for you.
- Lower trading fees that don’t eat into your wins
Fees matter because every percentage point you pay is one less in your pocket after a winning trade. Delta Exchange offers competitive taker and maker fees, plus a fee cap on options that limits how much you pay on low premium trades.
This helps keep costs predictable, whether you’re trading Bitcoin or ETH futures and options. Traders who place frequent trades or use multi-leg strategies on the Indian crypto exchange can keep more of their gains, rather than having them eaten up by trading fees.
- Strategy Builder for practical trading plans
Strategy planning can get messy if the platform doesn’t help you visualize outcomes. Delta Exchange offers tools that let you craft crypto F&O setups with clear strike choices and expiries, plus daily, weekly, and monthly options for more precise timing. This helps you conveniently plan spreads, straddles, or hedges.
- Compliance and risk measures to know
It’s one thing to trade, another to trust the platform doing it. Delta Exchange is registered with India’s Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) and follows local KYC and AML rules.
For risk management, the platform supports:
- Margin controls and stop-loss tools that help you manage positions while you trade Bitcoin or other crypto derivatives.
- Demo account to practice trades and understand the market without real money.
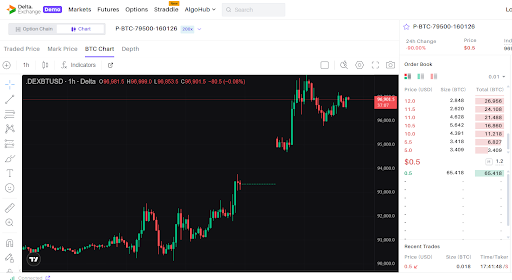
- Payoff charts show you how your trade will play out with breakeven points and maximum P&L.
This way, you can study your crypto trading strategy better before finalizing the trade.
Apart from these, Delta also offers leverage up to 200X – a good way to amplify your profits if the market moves in your favor.
The Bottomline
Indian crypto traders have moved far past the buy-and-hold phase. Spot crypto trading still has its place, yet most active users now want faster ways to make money from price swings, not wait months for a rally.
That’s where crypto F&O, spreads, and short-term setups step in. You want tools that let you react within minutes, control risk, and lock gains when the move shows up.
Platforms that only support basic coin buying just can’t keep up with that style of trading. Serious traders want flexibility, speed, and ways to work with volatility, not sit through it – and Delta Exchange caters to such traders well.
Disclaimer: Crypto trading carries inherent risks due to its high volatility. This article is for informational purposes only. Kindly do your own research before making any investment decisions.
Blockchain
MoonExe Aligns With the Next Phase of Stablecoin Payments as Global Regulation Accelerates

MoonExe today reaffirmed its strategic focus on stablecoin-powered payment infrastructure as global regulatory clarity continues to accelerate across major financial jurisdictions.
Regulators worldwide are advancing frameworks that formally recognize stablecoins as legitimate instruments for payment, settlement, and treasury operations. Legislative initiatives in the United States, expanded licensing regimes in Asia, and structured compliance approaches in other regions are collectively signaling a transition from experimental adoption to regulated, real-world deployment.
As stablecoins move deeper into mainstream financial infrastructure, demand is increasing for platforms capable of delivering real-time liquidity, transparent pricing, and verifiable settlement. MoonExe’s Exchange Finance (ExFi) model is designed to address these needs by enabling stablecoin-based currency conversions that operate continuously, without dependence on traditional banking cut-off times or geographic limitations.
The platform focuses on facilitating efficient value movement while maintaining transparency through public blockchain records. Transactions executed within the MoonExe ecosystem can be independently verified via standard blockchain explorers, reinforcing confidence through auditable, immutable data.
In parallel with regulatory progress, market participants are increasingly prioritizing infrastructure reliability over speculative activity. Stablecoins are being evaluated less as alternative assets and more as operational tools capable of supporting cross-border payments, digital commerce, and treasury flows.
MoonExe continues to expand its infrastructure and partnerships to support this evolution, positioning itself as part of the foundational layer required for stablecoins to function at global scale.
For more information about MoonExe and its stablecoin payment infrastructure, visit https://moonexe.com/
Blockchain
Playmaker to Launch in Q2 2026 as Midas Labs Expands Its AI-Powered Game Creation Ecosystem

Midas Labs, a UK-based Web3 technology company, has announced the upcoming launch of Playmaker, an AI-powered game creation and launchpad platform scheduled for Q2 2026. The platform is designed to lower barriers to game development and funding, operating as a core product within the UNIFI-powered Midas ecosystem.
Playmaker will provide creators, indie studios, and early-stage visionaries with an integrated environment to ideate, build, fund, and publish games without the traditional constraints of large teams or complex technical infrastructure. By combining AI-assisted creation tools with a structured launchpad and marketplace, the platform aims to streamline the path from concept to live product.
According to Jonathan Wheatley, Chief Marketing Officer of Midas Labs, Playmaker represents a natural progression of the company’s ecosystem strategy.
“Playmaker is about enabling participation at every level — from creators and developers to early supporters and players,” said Wheatley. “By integrating AI-driven creation with funding and publishing infrastructure, we’re building a system that allows ideas to move efficiently from concept to execution.”
The platform is powered by the $PLAY token, a fixed-supply utility asset used for project participation, creator payments, marketplace transactions, and ecosystem services. $PLAY operates within the broader UNIFI ecosystem, where UNIFI serves as the access and conversion layer, reinforcing liquidity and alignment across Midas Labs’ products.
Midas Labs has structured Playmaker’s token economy around a non-mintable, scarcity-driven model, designed to support long-term sustainability as platform adoption increases.
The Playmaker launch builds on recent Midas Labs milestones, including the expansion of the Midas Play Marketplace, multiple game releases, ecosystem partnerships, and the rollout of UNIFI staking infrastructure. Together, these components form a vertically integrated environment linking creation, funding, distribution, and participation.
Playmaker is scheduled to go live in Q2 2026, with phased ecosystem access beginning with early contributors before expanding globally.
About Midas Labs
Midas Labs is a United Kingdom–based Web3 technology company focused on building scalable digital ecosystems across gaming, AI, and creator-driven platforms. Powered by the UNIFI token, Midas Labs develops infrastructure designed for long-term participation, real utility, and sustainable growth.
-

 Crypto4 years ago
Crypto4 years agoCardalonia Aiming To Become The Biggest Metaverse Project On Cardano
-

 Press Release5 years ago
Press Release5 years agoP2P2C BREAKTHROUGH CREATES A CONNECTION BETWEEN ETM TOKEN AND THE SUPER PROFITABLE MARKET
-

 Blockchain6 years ago
Blockchain6 years agoWOM Protocol partners with CoinPayments, the world’s largest cryptocurrency payments processor
-

 Press Release5 years ago
Press Release5 years agoETHERSMART DEVELOPER’S VISION MADE FINTECH COMPANY BECOME DUBAI’S TOP DIGITAL BANK
-

 Press Release5 years ago
Press Release5 years agoProject Quantum – Decentralised AAA Gaming
-

 Blockchain6 years ago
Blockchain6 years agoWOM Protocol Recommended by Premier Crypto Analyst as only full featured project for August
-

 Press Release5 years ago
Press Release5 years agoETHERSMART DEVELOPER’S VISION MADE FINTECH COMPANY BECOME DUBAI’S TOP DIGITAL BANK
-

 Blockchain6 years ago
Blockchain6 years ago1.5 Times More Bitcoin is purchased by Grayscale Than Daily Mined Coins