Financial
Analysis of Curve Finance Reentrancy Attack

In July 2023, the Curve Finance reentrancy attack posed a significant security challenge for the leading decentralized finance (DeFi) platform, Curve Finance.
A reentrancy vulnerability within its system was exploited, leading to substantial financial losses across multiple DeFi projects.
We will now explore the vulnerability’s origins, its discovery, and the subsequent steps taken by Curve Finance and the broader DeFi community to address the security lapse.
What is Reentrancy?
On DeFi platforms, reentrancy attacks are malicious vulnerabilities in which a function is indirectly executed by itself before the initial execution is complete.
Such recursion may result in unwanted transactions that exploit smart contract flaws.
In the context of blockchain and Ethereum, in which Curve Finance operates, these flaws can cause significant financial damage due to the irreversible nature of transactions.
Reentrancy occurs when functions call other, untrusted contracts before resolving their effects (such as updating balances), allowing the external contract to re-enter the original function and causing logical disruptions.
For instance, this can lead to several withdrawals from the same deposit, depleting money that ought to be safeguarded.
Historical Context and Previous Incidents
The infamous DAO attack in 2016 was a landmark incident involving a reentrancy exploit, where an attacker drained around a third of the DAO’s funds by repeatedly recalling a function to withdraw Ether.
This event not only led to a significant financial loss but also prompted a hard fork in Ethereum, highlighting the critical importance of secure smart contract design.
Since then, the Ethereum community has prioritized enhancing security measures, yet reentrancy remains a daunting challenge. Various other incidents across the DeFi landscape have echoed the persistent vulnerability to such attacks, underscoring an ongoing battle against exploits in complex smart contract interactions.
This context sets the stage for understanding the recent incident with Curve Finance, in which similar vulnerabilities were exploited due to outdated compiler versions in their smart contracts.
To protect against changing threats in the DeFi sector, the incident serves as a clear reminder of the need for strict security protocols as well as ongoing updates and audits of the smart contract codebase.
Discovery and Response to the Curve Finance Vulnerability
The reentrancy vulnerability in Curve Finance was identified during a routine security audit by an independent developer who was examining the code for potential flaws.
Initial Discovery of the Bug
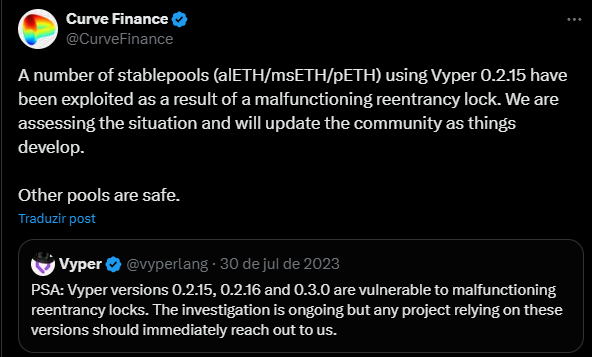
The vulnerability stemmed from the use of outdated versions of the Vyper compiler, versions 0.2.15, 0.2.16, and 0.3.0, which failed to implement effective reentrancy guards.
This oversight left certain smart contracts open to exploitation, particularly those involving transactions linked to native ETH or tokens adhering to the ERC-777 standard.
Curve Finance and Vyper posted on the social platform X stating:
Technical Analysis of the Vulnerability
The specific flaw allowed attackers to manipulate the contract’s functions to withdraw funds repeatedly before the contract state could be updated to reflect each transaction.
This type of attack exploits the gap between the initiation of a contract call and the state update, a critical period during which the contract is vulnerable.
The Vyper programming language, known for its Python-like syntax and targeted at Ethereum’s virtual machine, was central to the issue.
The language’s updates had not adequately addressed the reentrancy guard, which should prevent multiple entries into vulnerable functions during a single transaction.

Curve Finance’s Immediate Actions
Upon discovery, Curve Finance swiftly responded by halting affected transactions and patching the vulnerability. They updated the compiler and adjusted the smart contracts to include enhanced security checks.
Additionally, the platform launched a white-hat program, encouraging ethical hackers to find and report vulnerabilities in return for bounties. This initiative not only helped fix the immediate issue but also bolstered the platform’s defenses against future attacks.
The response was part of a broader effort to reinforce trust and security within the Curve Finance ecosystem and the DeFi community at large.
Implications for the DeFi Ecosystem
The revelation of the reentrancy vulnerability in Curve Finance triggered a swift and coordinated response across the DeFi community. Various platforms initiated reviews of their protocols, especially those written in Vyper or similar languages prone to similar issues.
Immediate Community Reaction and Long-term Impact on DeFi Security
The incident fueled a widespread reassessment of security strategies within the DeFi space, with many platforms accelerating their security audits and patch implementations to fortify their systems against similar vulnerabilities.
The incident involving Curve Finance is an important reminder of the security risks that are part and parcel of the DeFi industry.
It emphasized the need for continuous improvement in smart contract design and validation techniques. As a result, there has been a significant increase in the adoption of more rigorous testing environments and security frameworks, which are critical for maintaining trust and stability in DeFi.
The incident has also underscored the necessity of community vigilance and the role of white-hat hackers in detecting and mitigating possible dangers before they can cause widespread damage.
Strengthening DeFi Security
To mitigate risks such as reentrancy attacks, developers must implement best practices in smart contract design, such as the checks-effects-interactions pattern, which organizes code to make unexpected reentries difficult.
Regular security audits and the integration of security tools that automate the detection of common vulnerabilities are crucial.
Developers are also encouraged to use updated and secure compilers to avoid introducing flaws that can be exploited.
Strategic Recommendations for DeFi Platforms
DeFi platforms should establish robust security frameworks that include continuous monitoring and rapid response systems.
Encouraging a culture of security within the development community and incentivizing the disclosure of potential vulnerabilities through bug bounty programs are effective strategies.
These efforts enhance not only the security of individual platforms but also contribute to the resilience and trustworthiness of the entire DeFi ecosystem.
Enhancing DeFi Security Post-Curve Finance Reentrancy Attack
The reentrancy vulnerability exposed in Curve Finance served as a critical wake-up call for the DeFi sector.
It underscored the perpetual need for vigilance, robust security protocols, and the proactive involvement of the community in safeguarding digital assets.
The occurrence sparked a round of security reassessments across several DeFi platforms, emphasizing the significance of ongoing development in smart contract design and implementation.
DeFi platforms must adopt secure coding practices, prioritize thorough and frequent audits, and keep up with the most recent advancements in smart contract security if they are to improve security measures.
The implementation of automated vulnerability detection tools and the promotion of a security-first approach among developers will be pivotal in averting such incidents.
Final thoughts and FAQ:
The incident highlights the effectiveness of community-driven security enhancements, such as bug bounty programs and white-hat initiatives, which not only help in identifying vulnerabilities but also foster a collaborative approach to security.
As DeFi continues to evolve, the commitment to implementing these best practices will be pivotal in shaping its resilience and ensuring the trust of users and investors in this dynamic and promising sector of the financial industry.
- What is a reentrancy attack in DeFi?
When a malicious actor takes advantage of a smart contract vulnerability that allows a function to be called more than once before its initial invocation is finished, it can result in unauthorized actions like multiple withdrawals. This type of attack is known as a reentrancy attack in the context of decentralized finance (DeFi). - How was the Curve Finance reentrancy vulnerability discovered?
When an independent developer conducted a routine audit, they discovered the Curve Finance reentrancy vulnerability. Outdated versions of the Vyper compiler did not properly implement reentrancy guards, leaving smart contracts vulnerable to attacks. - What steps did Curve Finance take in response to the vulnerability?
The affected smart contracts were updated, security measures were strengthened, and Curve Finance introduced a bug bounty program to incentivize the community to report possible security flaws. Curve Finance swiftly addressed the vulnerability. - What are the best practices to prevent reentrancy attacks in DeFi?
Best practices include using the checks-effects-interactions pattern in smart contract development, conducting regular and comprehensive security audits, and employing up-to-date and secure compilers to minimize risks. - What impact did the reentrancy exploit have on the DeFi ecosystem?
The exploit led to significant financial losses and prompted a broader reassessment of security protocols across multiple DeFi platforms. It highlighted the need for continuous improvement in security practices and community engagement in the security process.
Crypto Currency
Atlas of USA Positions Itself as a Narrative-Driven Digital Asset Tied to American Identity

Atlas of USA (ATLAS) is emerging as a narrative-focused crypto project that blends digital asset experimentation with themes centered on American identity, decentralization, and community coordination. As attention around politically themed and culture-driven tokens continues to fluctuate across the crypto market, Atlas of USA is attempting to differentiate itself through branding, symbolism, and grassroots engagement rather than short-term speculation.
Unlike infrastructure-heavy blockchain projects, Atlas of USA presents itself primarily as a narrative and community-oriented digital asset. The project emphasizes symbolic alignment with U.S. economic ideals, decentralization, and collective participation, positioning ATLAS as a token shaped more by social coordination than technical complexity.
Token Structure and Supply Characteristics
ATLAS operates as a fungible crypto asset with a fixed supply model designed to avoid inflationary pressure. The project does not promote emissions schedules or yield-driven incentives, instead focusing on ownership distribution and long-term holding behavior. This structure reflects a broader trend among narrative tokens that prioritize scarcity and cultural signaling over utility-based tokenomics.
Market data shows that ATLAS trading activity has remained episodic, with volume spikes often aligning with broader shifts in sentiment around politically themed or U.S.-centric crypto narratives. This behavior is consistent with other community-driven tokens whose momentum is closely tied to social engagement rather than protocol upgrades.
Community-First Positioning
A core component of the Atlas of USA approach is its emphasis on community participation. The project frames token holders as contributors to a shared narrative rather than passive investors. Messaging across community channels highlights coordination, visibility, and grassroots amplification as central drivers of growth.
This positioning aligns with a wider crypto trend where narrative cohesion and online identity increasingly influence token awareness. Rather than promising technological breakthroughs, Atlas of USA leans into symbolism and collective recognition, allowing the market to assign meaning organically.
Market Context and Competitive Landscape
Atlas of USA exists within a crowded category of narrative-based digital assets that draw inspiration from national identity, political discourse, or cultural movements. While competition in this segment is high, ATLAS attempts to stand out by maintaining a clear thematic focus and avoiding overextension into unrelated utility claims.
From a market perspective, ATLAS remains sensitive to sentiment cycles. Periods of increased visibility tend to coincide with broader discussions around U.S. economic policy, decentralization, or digital sovereignty within crypto communities.
Outlook
Atlas of USA represents an example of how crypto assets can function as social and narrative instruments rather than purely technical products. Its future trajectory will likely depend on sustained community engagement, consistent messaging, and its ability to remain relevant within shifting cultural conversations.
As the crypto market continues to fragment into utility-driven protocols and narrative-driven tokens, projects like Atlas of USA highlight how identity and coordination remain powerful forces in digital asset ecosystems.
Crypto
Binance Founder CZ Calls for Industry-Wide Action After $50 Million Address Poisoning Scam

Binance co-founder Changpeng Zhao has urged the crypto industry to adopt unified defenses against address poisoning scams following a $50 million theft involving a single mistaken transaction. The incident, which occurred on December 20, highlights how even experienced traders remain vulnerable to increasingly sophisticated wallet manipulation tactics.
Address poisoning is a form of phishing that exploits how crypto wallets display shortened addresses. By mimicking the first and last characters of a legitimate address, attackers trick users into sending funds to fraudulent destinations that appear familiar at a glance.
How the $50 Million Scam Unfolded
According to on-chain data, the victim began with a standard precaution: a small test transfer. On December 20, the trader sent 50 USDT to what they believed was the correct address. Twenty-six minutes later, confident the destination was verified, they transferred 49,999,950 USDT.
Unbeknownst to the sender, the second transaction went to a scammer-controlled address. The fraudulent address matched the first five and last four characters of the intended destination, differing only in the middle portion—exactly the segment most wallets hide behind ellipses.
This visual similarity allowed the attacker to exploit common user behavior, where traders confirm only the beginning and end of an address rather than the full string.
After receiving the funds, the attacker quickly converted the stolen USDT into DAI, then swapped it for approximately 16,690 ETH. The ETH was later deposited into Tornado Cash, a privacy protocol frequently used to obscure transaction trails. The victim subsequently offered a $1 million on-chain bounty in an attempt to recover the funds.
CZ’s Proposal to Stop Address Poisoning
In response to the incident, Changpeng Zhao proposed three industry-wide countermeasures designed to reduce address poisoning risk across wallets and platforms.
First, Zhao called for automatic detection of suspected poison addresses within wallets. These systems would flag addresses that closely resemble previously used destinations and warn users before transactions are signed.
Second, he suggested real-time sharing of blacklisted scam addresses across the industry. A coordinated database could allow wallets and exchanges to instantly recognize known malicious addresses and alert users.
Third, Zhao recommended filtering spam transactions from wallet histories. Since attackers often seed wallet activity with fake transactions to create misleading address records, hiding or isolating these entries could significantly reduce the effectiveness of poisoning attempts.
Binance Wallet already implements warnings for suspected poison addresses, but Zhao emphasized that isolated solutions are not enough. Address poisoning, he argued, requires a collective response across the crypto ecosystem.
Why Address Poisoning Is a Growing Threat
The incident underscores a broader trend in crypto-related crime. Phishing attacks were the most costly category of crypto theft in 2024, according to blockchain security firm CertiK. Attackers stole more than $1 billion across 296 phishing incidents that year alone.
In 2025, address poisoning accounted for over 10% of wallet drain incidents, reflecting both its effectiveness and ease of execution. The technique does not rely on smart contract vulnerabilities or malware, making it harder to detect with traditional security tools.
One notable case in May 2024 involved a victim who lost $68 million worth of wrapped Bitcoin through address poisoning. In that instance, the attacker eventually returned the funds after pressure from investigators, but such outcomes remain rare.
The Bigger Picture for Crypto Security
Total cryptocurrency theft reached an estimated $3.4 billion in 2025, reinforcing the urgency of improving user-level protections. As self-custody adoption grows, so does the responsibility placed on individuals to verify transactions accurately.
Address poisoning highlights a fundamental usability issue in crypto wallets: human-readable shortcuts can create dangerous blind spots. Without better safeguards, even cautious users can make irreversible mistakes in seconds.
Changpeng Zhao’s call for industry-wide standards reflects a growing consensus that security must evolve alongside adoption. Preventing address poisoning will likely depend not only on better tools, but on collaboration across wallets, exchanges, and blockchain infrastructure providers.
As crypto continues to move toward mainstream usage, reducing preventable losses may prove just as important as advancing new technologies.
Crypto
Trust Wallet Hack Today: Who Is at Risk After $6 Million Breach

A security incident involving the Trust Wallet browser extension has resulted in the loss of nearly $6 million worth of cryptocurrency, triggering concern across the crypto community during the holiday period. The breach highlights ongoing risks tied to browser-based wallets and the importance of rapid updates when vulnerabilities emerge.
According to Trust Wallet, the issue is limited to version 2.68 of its browser extension. Users of the Trust Wallet mobile application and those running other extension versions are not affected.
What happened with the Trust Wallet hack?
The vulnerability was first identified on December 24, when abnormal wallet activity began appearing on-chain. By December 25, blockchain analysts observed funds being drained from multiple wallets operating on Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana networks.
Independent investigator ZachXBT reported receiving messages from hundreds of users whose balances dropped suddenly without any outgoing transactions initiated by them. Community researchers later identified suspicious code within version 2.68 of the extension. The code allegedly redirected sensitive wallet data to a fake external website, giving attackers unauthorized access to user funds.
On-chain analysis suggests the stolen funds were routed through numerous addresses, making the total scope difficult to track precisely. Current estimates place losses at a minimum of $6 million.
Trust Wallet confirms extension vulnerability
Trust Wallet has acknowledged the incident and confirmed that only the 2.68 browser extension was compromised. The company instructed users to immediately stop using that version and upgrade to version 2.69, which it says resolves the issue.
The wallet provider stated that its security and support teams are actively investigating the breach and reaching out to affected users. While Trust Wallet has not yet confirmed whether compensation will be offered, it says impacted users are being guided through recovery and reporting steps.
What users should do immediately
Anyone who used the Trust Wallet browser extension is advised to take action without delay:
First, do not open the Trust Wallet extension on desktop devices if it is still enabled. This reduces the risk of further exposure.
Second, disable the extension immediately via the browser’s extensions settings.
Third, update only to version 2.69 and ensure the update is downloaded exclusively from the official Chrome Web Store. Users should double-check the version number after installation.
Finally, contact Trust Wallet support if any funds are missing. Providing transaction history and wallet details may help ongoing investigations.
Why this incident matters for crypto users
The Trust Wallet hack underscores the unique risks associated with browser extensions. Unlike hardware wallets or isolated mobile environments, browser-based wallets operate in a space frequently targeted by malicious code injections, phishing scripts, and supply-chain attacks.
Even well-established wallet providers can be exposed if a compromised update slips through. This incident reinforces the need for users to monitor wallet updates closely, limit hot wallet balances, and consider additional security measures for long-term holdings.
As investigations continue, Trust Wallet has stated it will release further updates. For now, the breach serves as a reminder that security hygiene — including timely updates and cautious extension use — remains critical in the crypto ecosystem.
-

 Crypto4 years ago
Crypto4 years agoCardalonia Aiming To Become The Biggest Metaverse Project On Cardano
-

 Press Release5 years ago
Press Release5 years agoP2P2C BREAKTHROUGH CREATES A CONNECTION BETWEEN ETM TOKEN AND THE SUPER PROFITABLE MARKET
-

 Blockchain6 years ago
Blockchain6 years agoWOM Protocol partners with CoinPayments, the world’s largest cryptocurrency payments processor
-

 Press Release5 years ago
Press Release5 years agoETHERSMART DEVELOPER’S VISION MADE FINTECH COMPANY BECOME DUBAI’S TOP DIGITAL BANK
-

 Press Release5 years ago
Press Release5 years agoProject Quantum – Decentralised AAA Gaming
-

 Blockchain6 years ago
Blockchain6 years agoWOM Protocol Recommended by Premier Crypto Analyst as only full featured project for August
-

 Press Release5 years ago
Press Release5 years agoETHERSMART DEVELOPER’S VISION MADE FINTECH COMPANY BECOME DUBAI’S TOP DIGITAL BANK
-

 Blockchain6 years ago
Blockchain6 years ago1.5 Times More Bitcoin is purchased by Grayscale Than Daily Mined Coins






